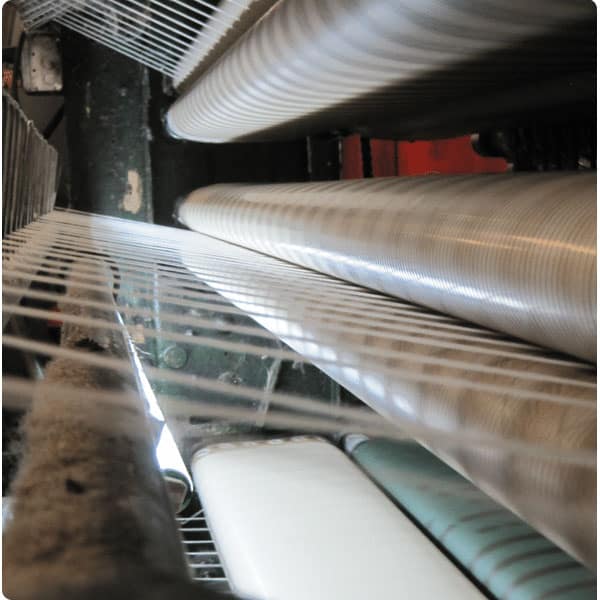
Carding refers to the crucial step that opens and aligns fibers into a parallel structure, preparing them for woolen spun yarn manufacturing. This process helps to remove any remaining impurities and prepares the fiber for spinning. It also determines the weight and thickness of the yarn, which is computer-regulated for precision.
Carding settings can be adjusted for fine, coarse, or mixed-micron fibers to maintain quality and consistency across woolen and man-made inputs. The carded wool yarn is known as pencil roving, a uniform, airy fiber bundle ready for spinning high-performance textile yarns.